General information
Parses the column that contains a list to have a single value in every cell.
Description
Brick Locations
Bricks → Transformation → Parse List
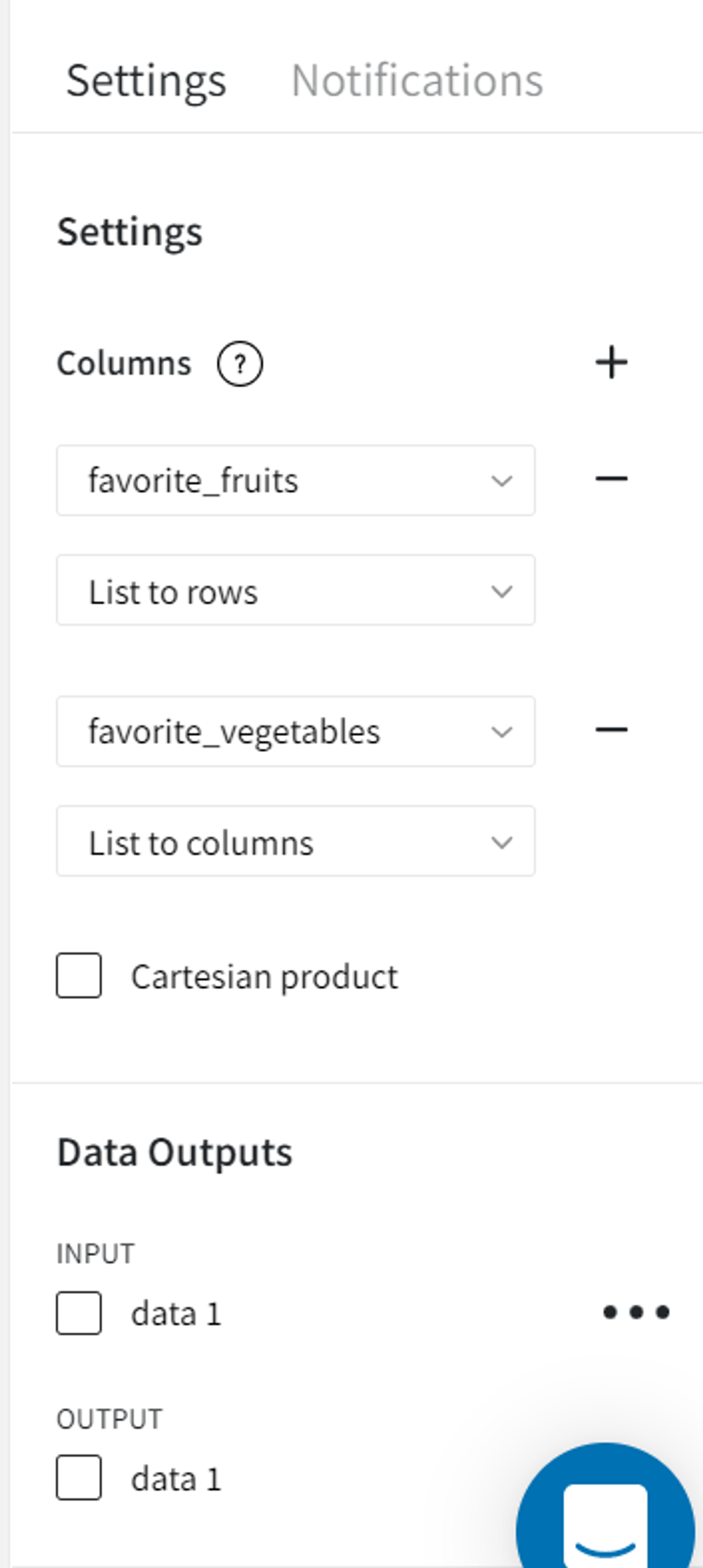
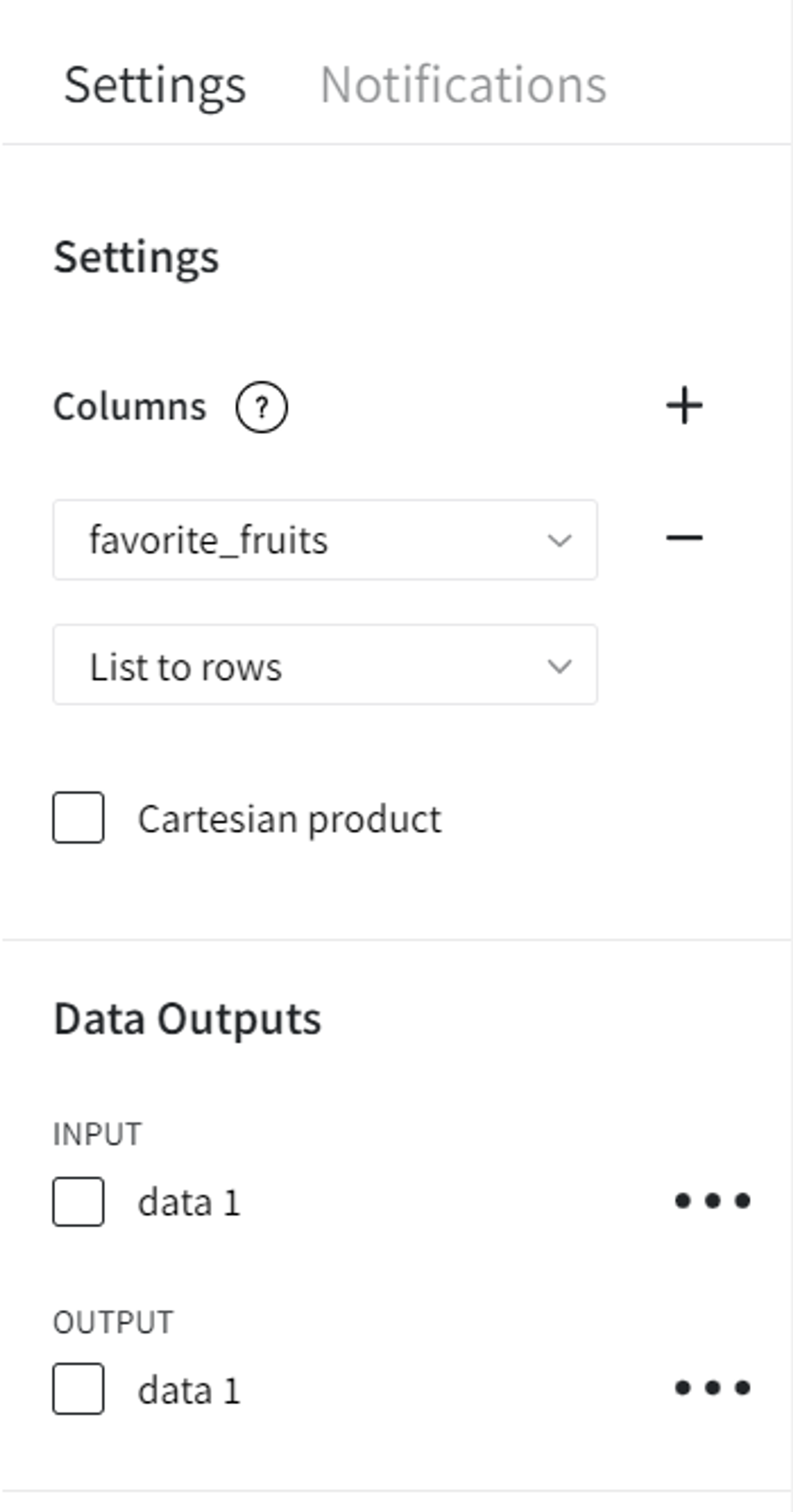
Brick Parameters
- Columns
- List to rows
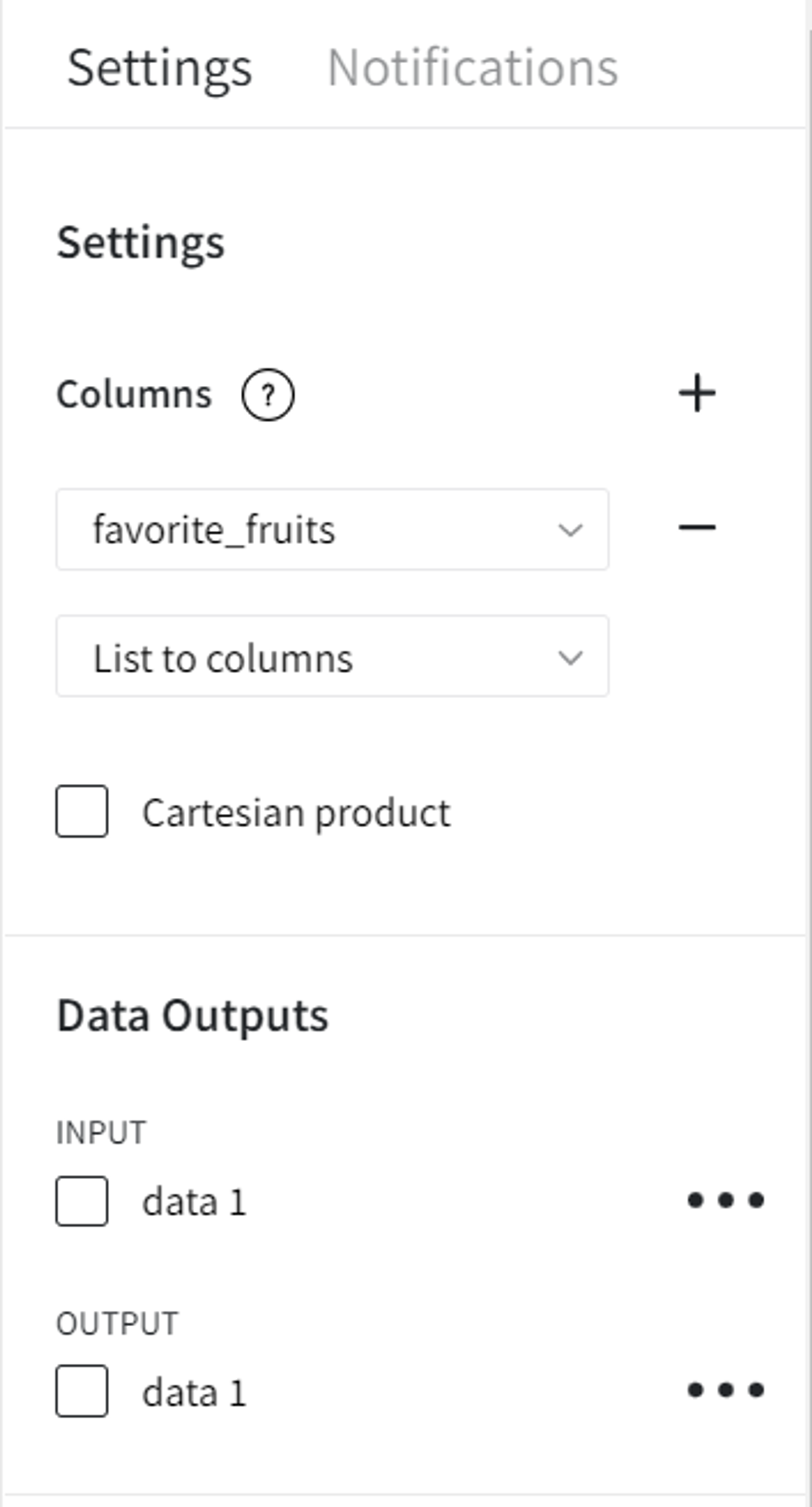
- List to columns
Columns of list type to parse. Multiple columns can be selected by clicking the + button.
Available transformation options:
- Cartesian product
A checkbox that enables to perform cartesian product between multiple columns with ‘List to rows’ transformations.
- Brick frozen
Enables frozen run for the brick.
Brick Inputs/Outputs
- Inputs
Brick takes the dataset
- Outputs
Brick produces the dataset with parsed list columns, which contains extra rows or columns depending on the transformation type
Example of usage
Let’s have a look at the example where we have a dataset that contains two columns with list values.
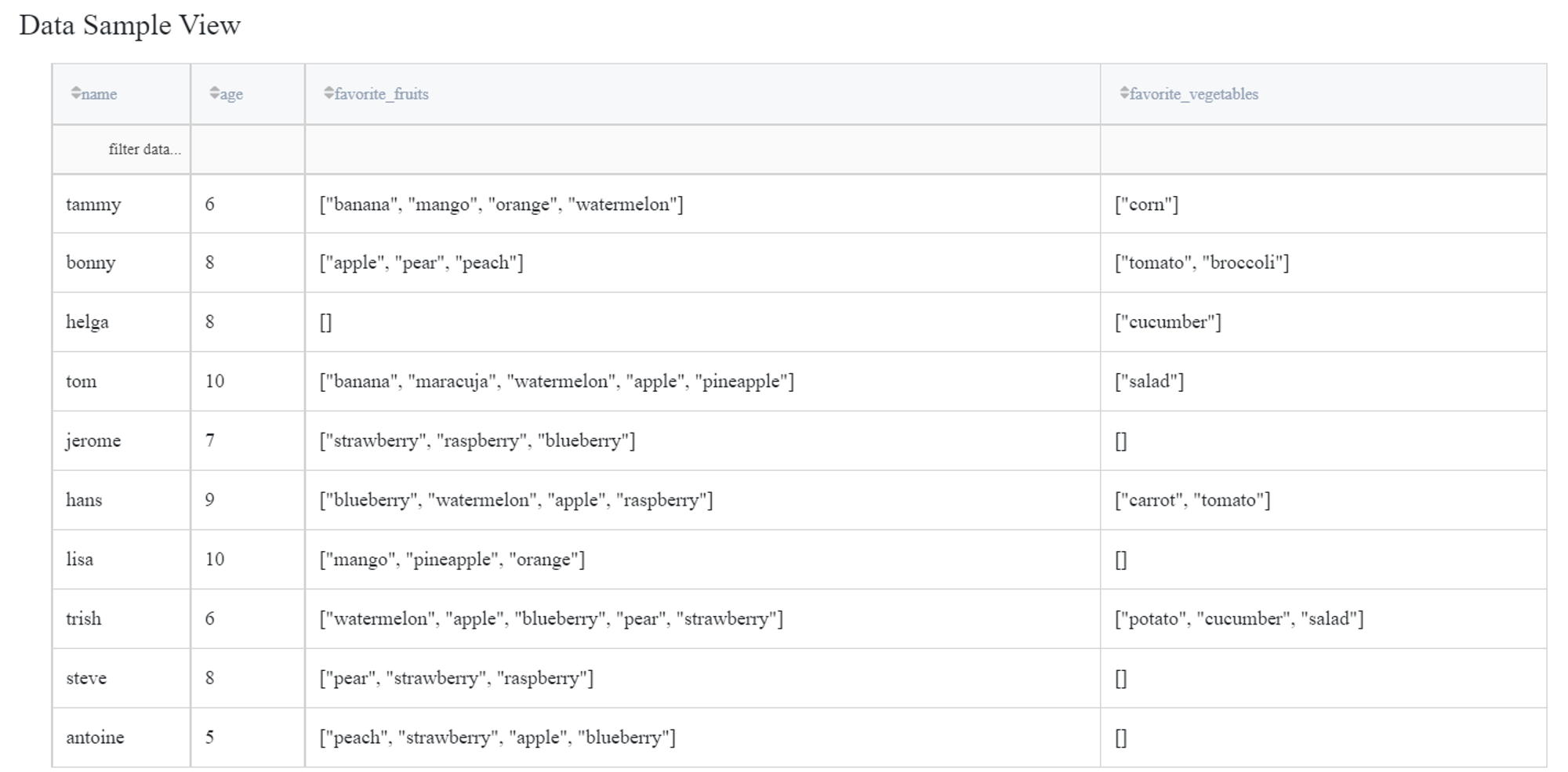
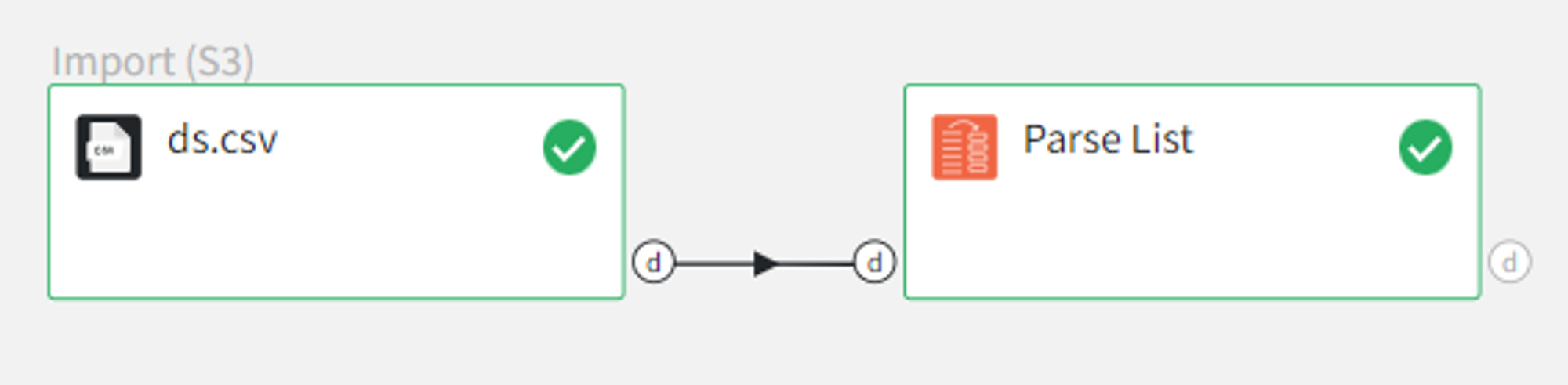
We can connect this dataset directly to the Parse List Brick.
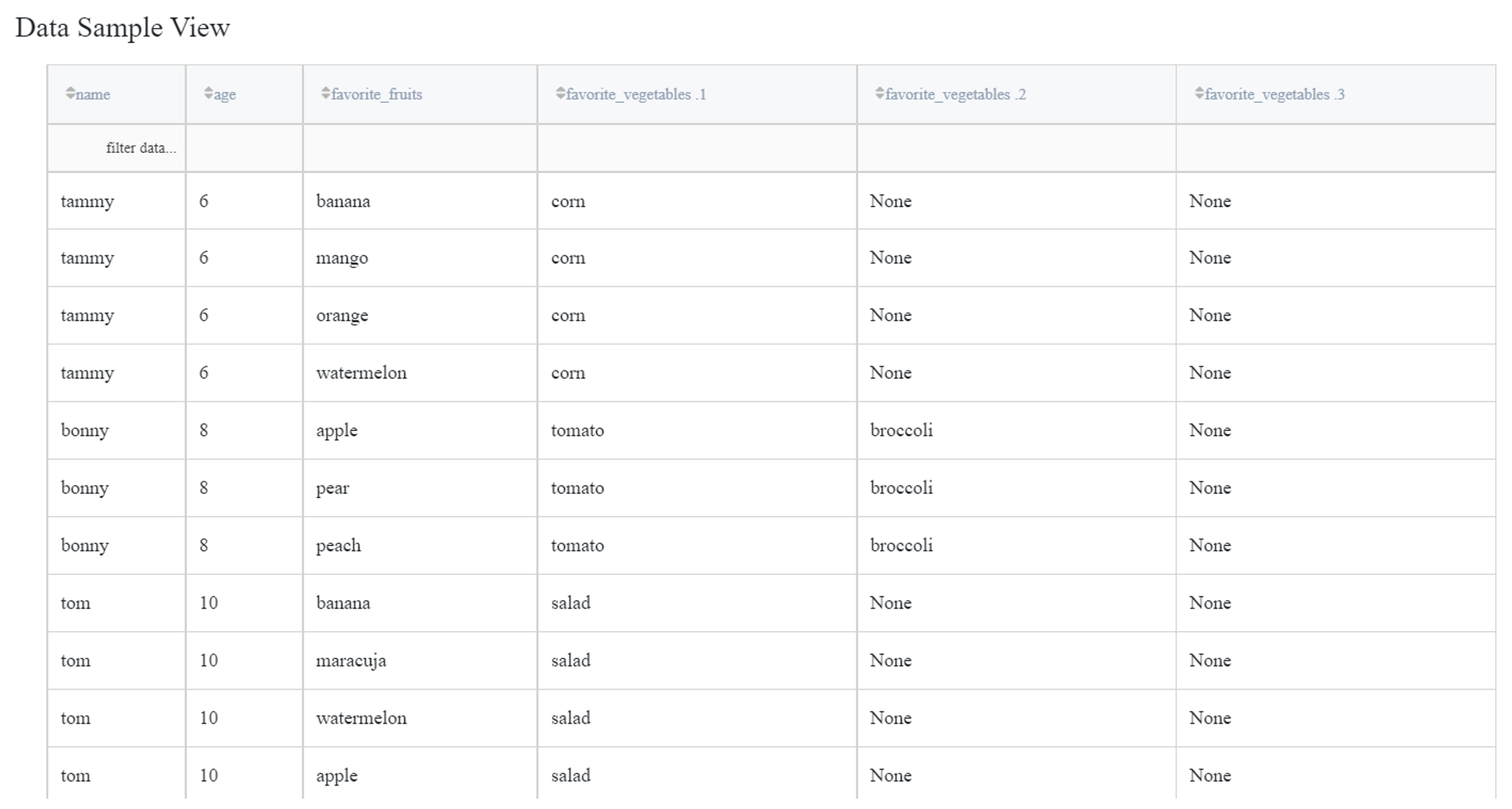
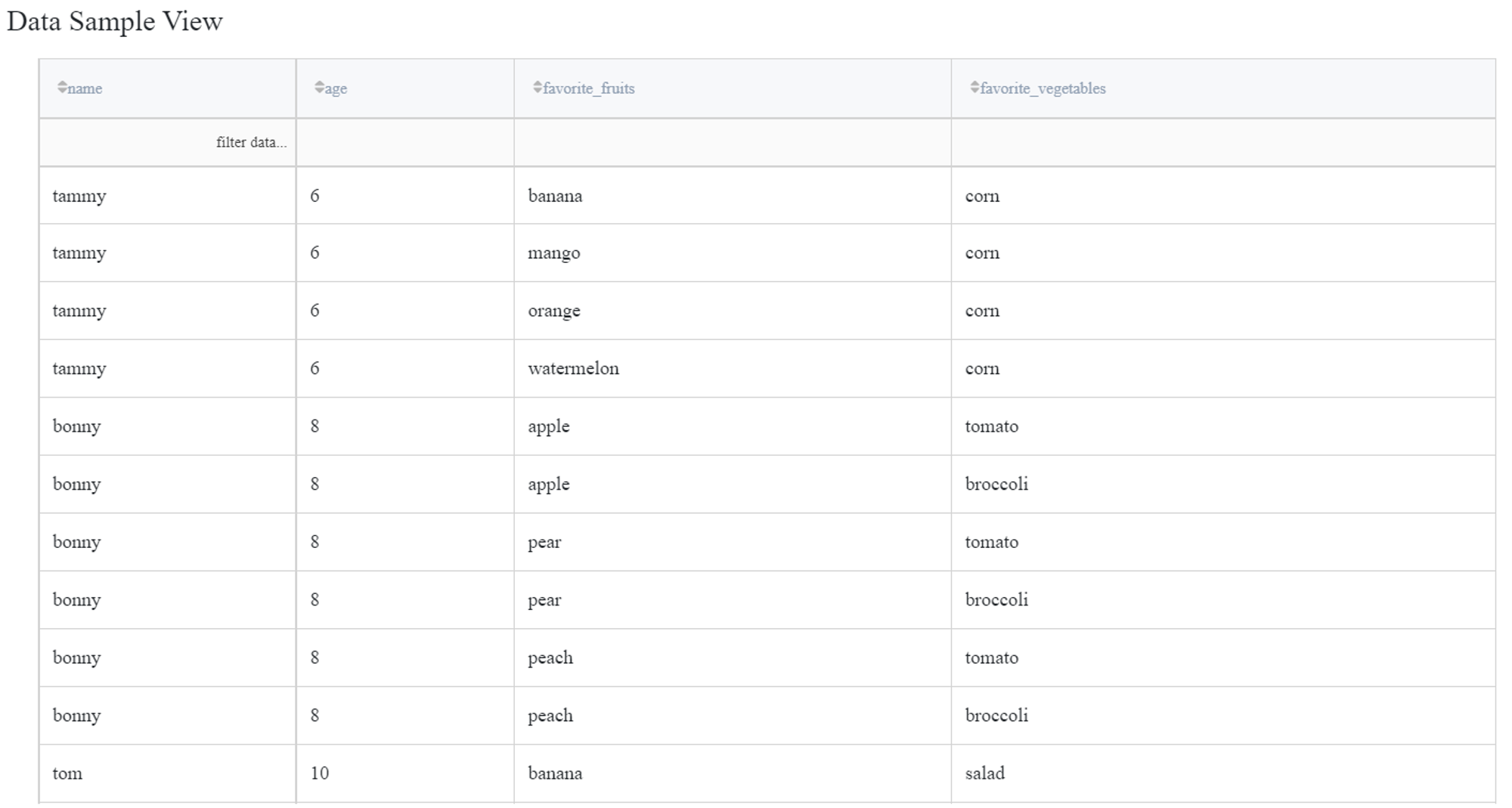
First, we can try to parse the column ‘favorite_fruits’ with the setting ‘List to rows’.
As a result, we get a dataset that has the list of selected column values located in separate rows with other features duplicated. You can view this dataset from the Data Outputs section.
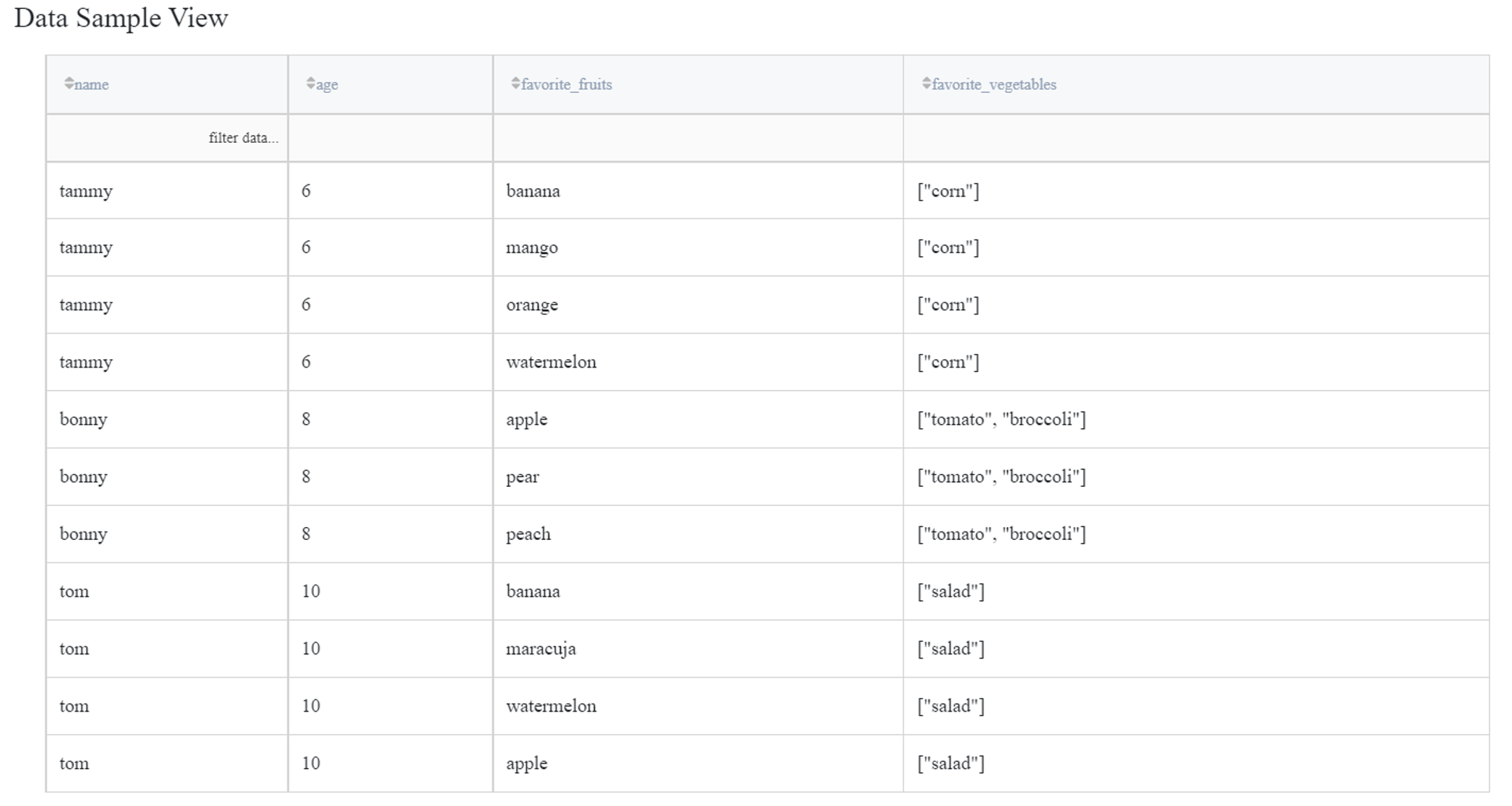
Note that the record with an empty list is absent in the resulting dataset.
If we select the ‘List to columns’ option instead, N new columns will be created in the output dataset, where N is a maximum list length. If for a sample the list length is less than N, then the corresponding columns are filled with None.
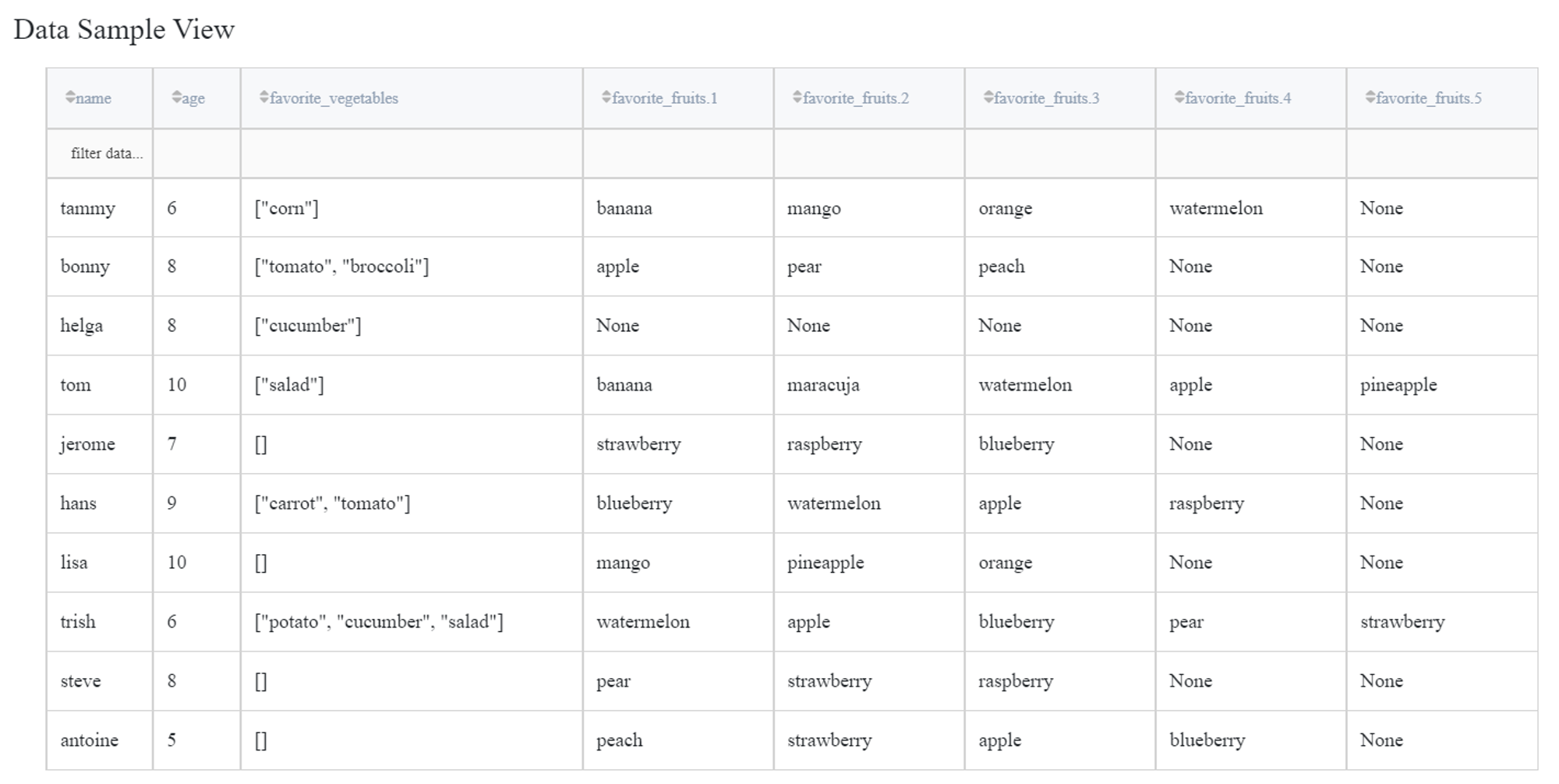
Now, let’s parse both columns with different settings.
If we select to parse both columns as ‘List to rows’ and uncheck ‘Cartesian product’, we get the warning.
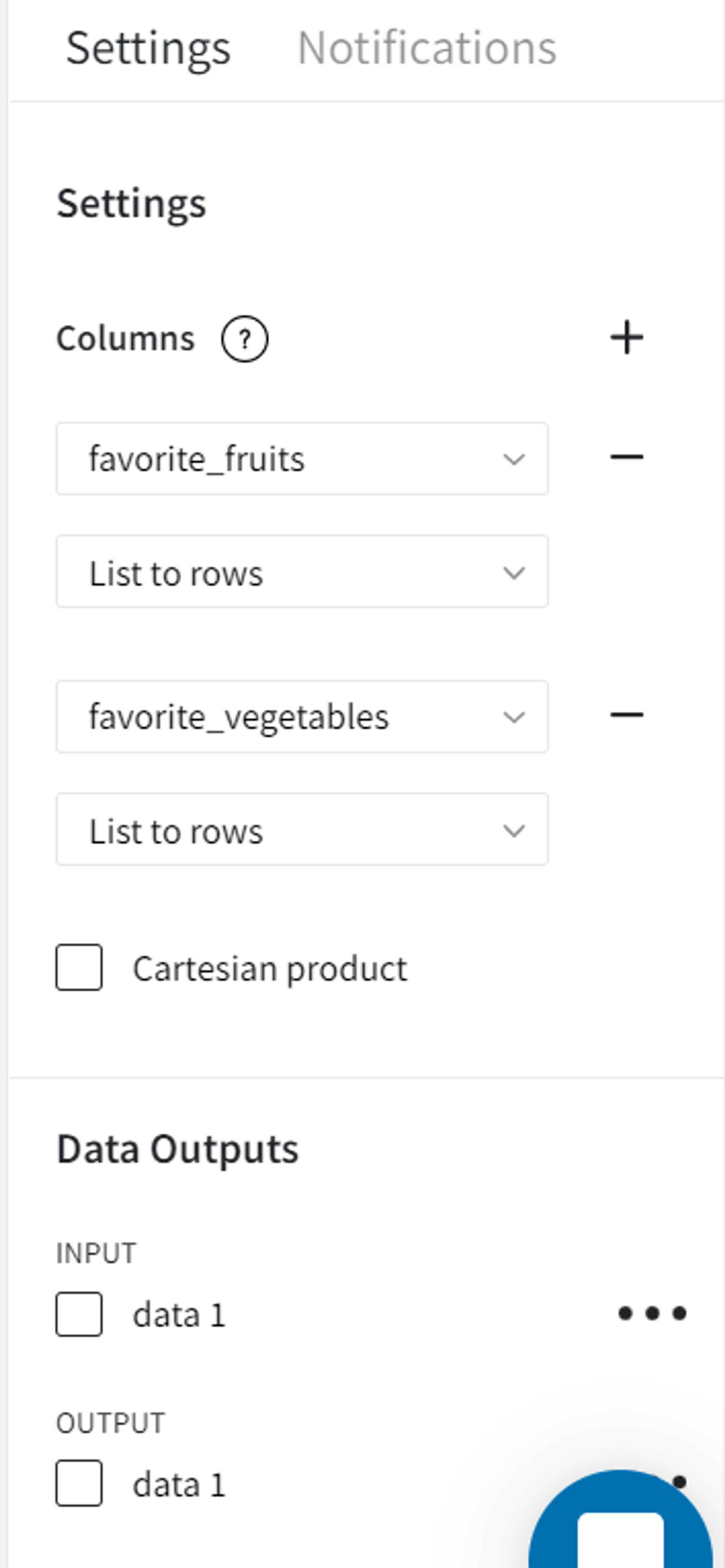
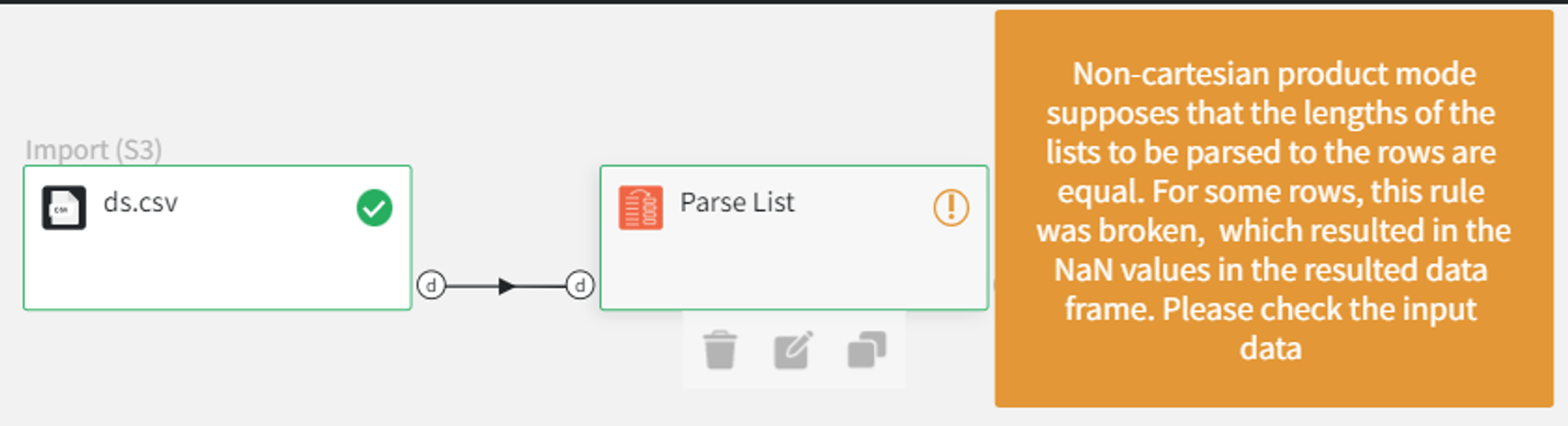
This happens because the non-cartesian product mode tries to combine values from lists pairwise. As the lists from the dataset have different lengths, the missing pair values are automatically filled with None.
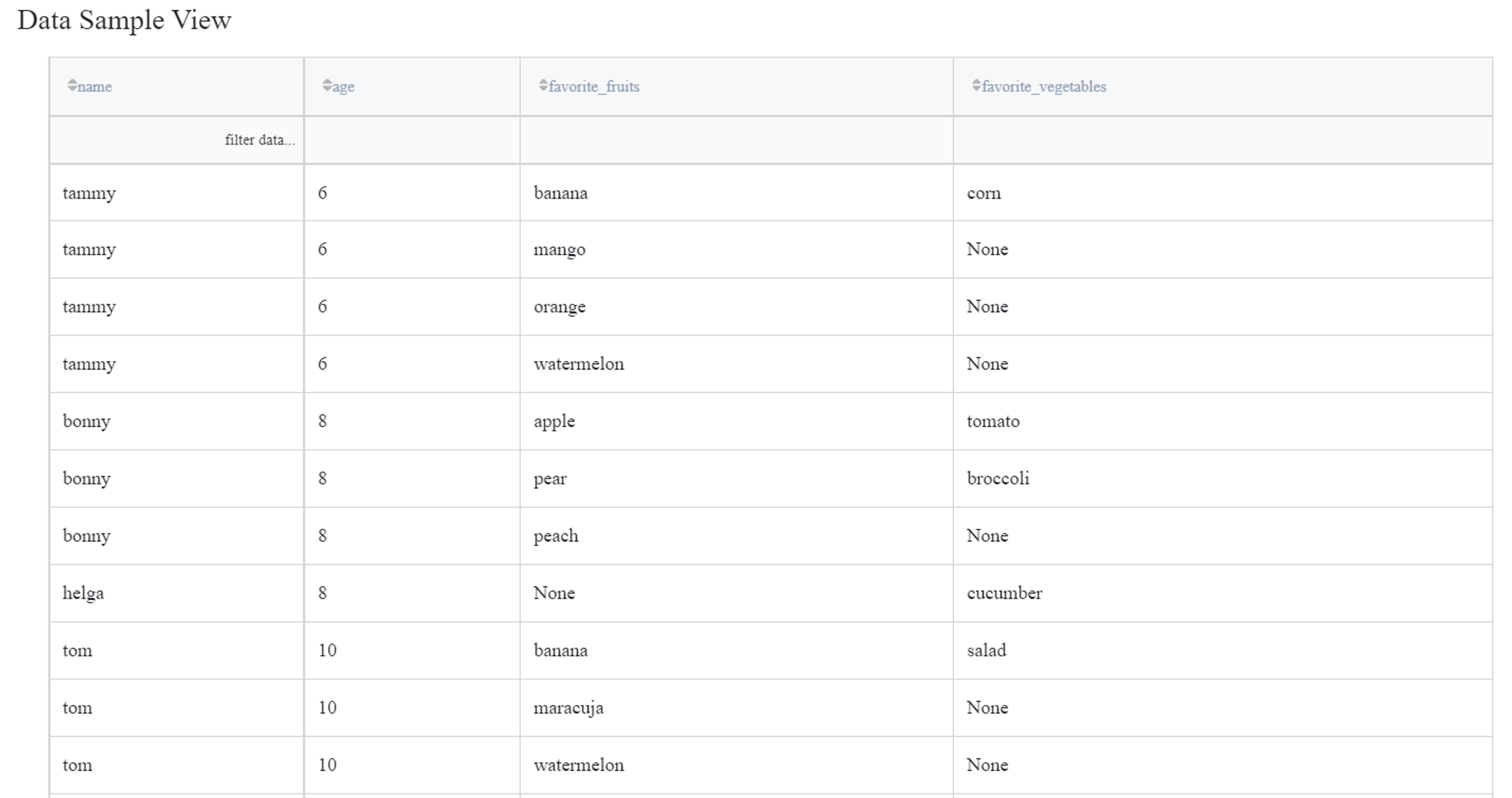
Checking ‘Cartesian product’ performs calculation of cartesian product between the selected lists for all records i.e. generates all the possible combinations of list values.
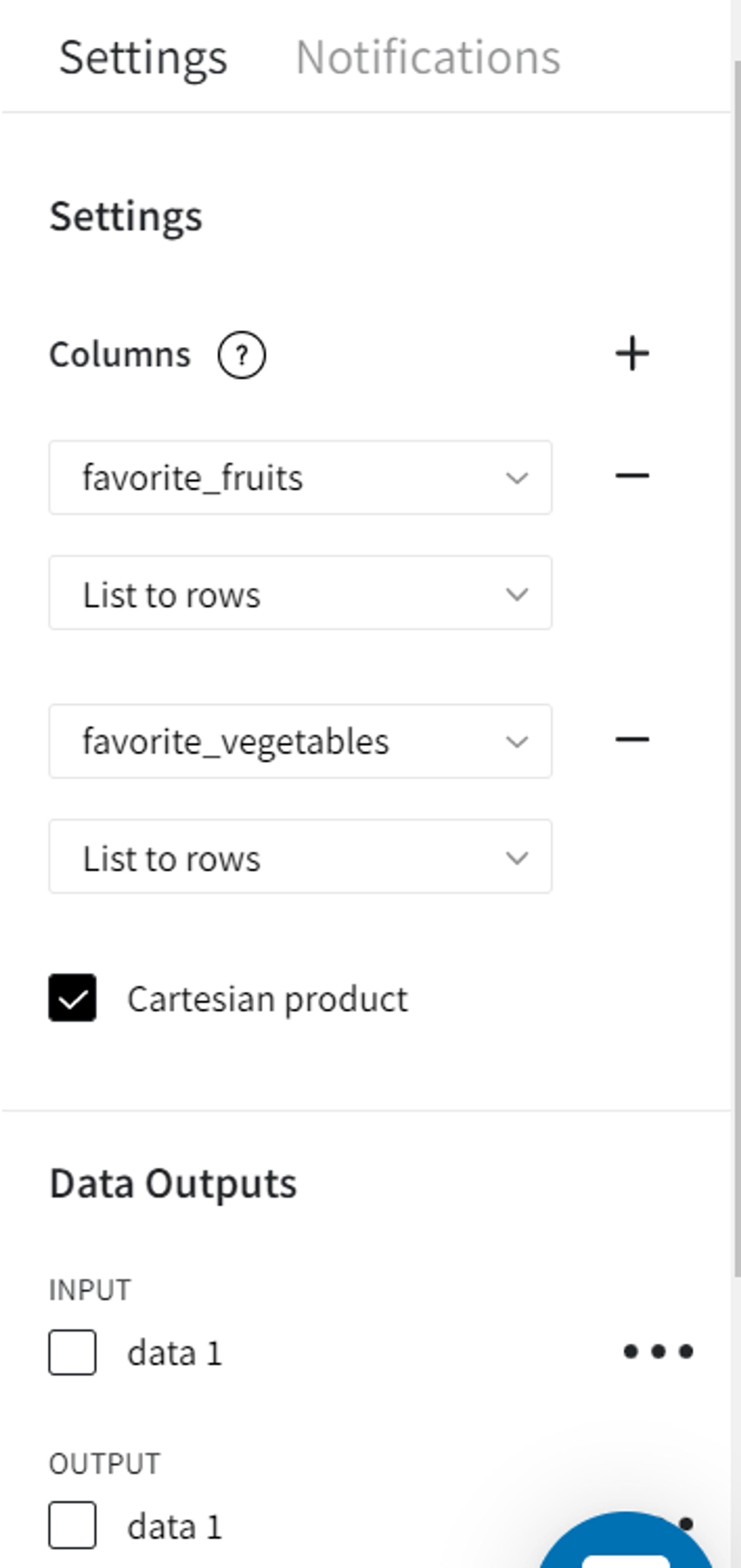
Note that when one of the lists is empty, the cartesian product cannot be calculated so the record is omitted.
If one column is parsed as ‘List to rows’ and another one as ‘List to columns’, then the resulting dataset will contain values from the first column in rows with the values from the second column in separate columns duplicated for each row.