General information
Prepare Future Dataset brick generates a future time series dataset for a trained Neural Prophet model.
Description
Brick Locations
Bricks → Machine Learning → Prepare Future Dataset
Brick Parameters
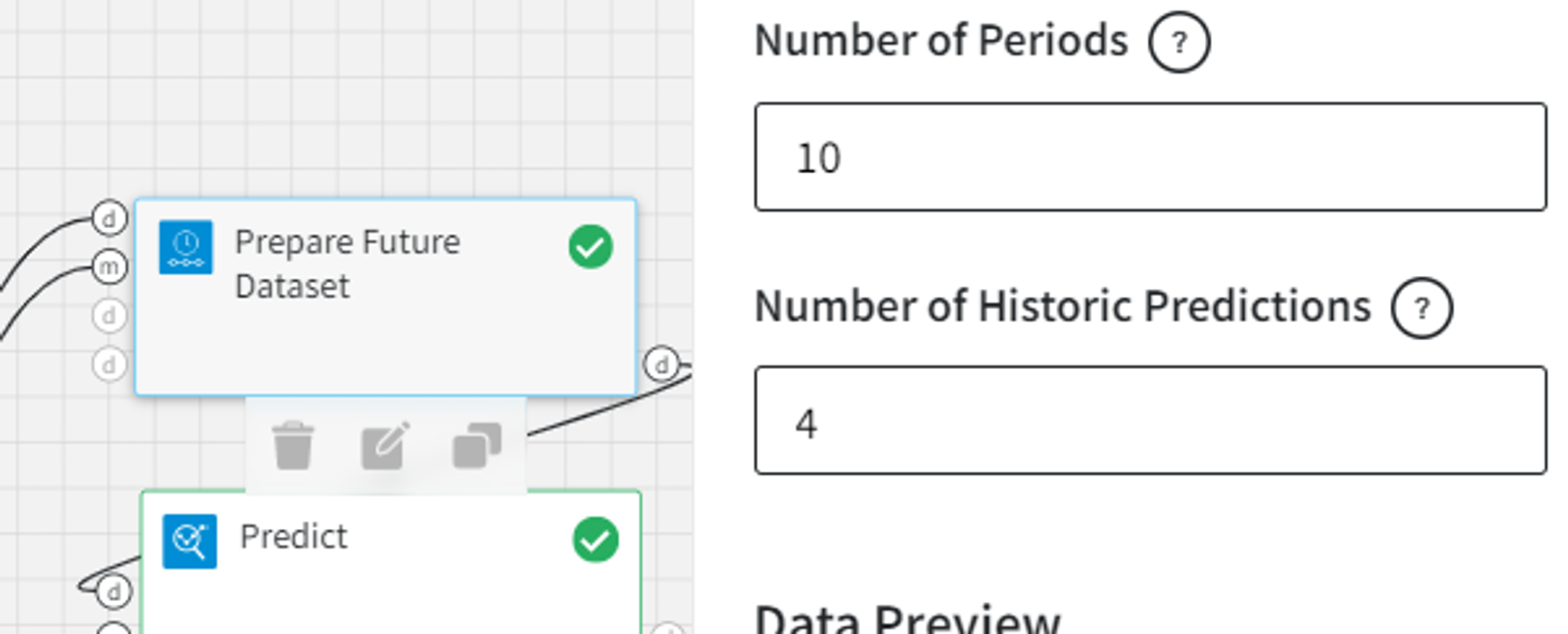
- Number of periods
The number of steps to extend the dataset into the future.
Note that this value is ignored when the auto-regression components are present in the trained input model. In this case, the number of periods is defined by the number of forecasts in the model.
- Number of historic predictions
The number of historic observances to include.
Future Regressors
- Datetime (optional)
A column from the optional future regressors input that contains the dates of the future observations. If not selected, the consecutive dates are generated based on the model’s training data.
Events
- Datetime
A column from the optional events input that contains the dates for the user-specific events for the forecast period.
- Events column
A column from the optional events input that specifies the names of the user-specific events.
Brick Inputs/Outputs
- Inputs
- data
- model
- optional future regressors
- optional events
Dataset to be extended into the future. If the auto-regression options are defined for the model or the Number of Historic predictions > 0, the input must contain all columns used for model fit. The columns that did not appear in the model configuration will be automatically filtered.
A trained Neural Prophet model.
This output is required if the input model was trained with future regressors. A future regressors dataframe must contain one column for each of the future regressors and optionally a datetime column if it is selected in the settings. All the other columns will be automatically filtered.
Future event occurrences corresponding to ’periods’ steps into the future. It must contain columns ‘Datetime’ and ‘Events column’, selected in the settings. If the events were specified for the model but this input is not connected, then the custom events will be treated as non-occurring in the future.
- Outputs
Brick returns a future dataset with new timestamps added to the historic data.
Example of usage
Here are examples of the Prepare Future Dataset brick usage.
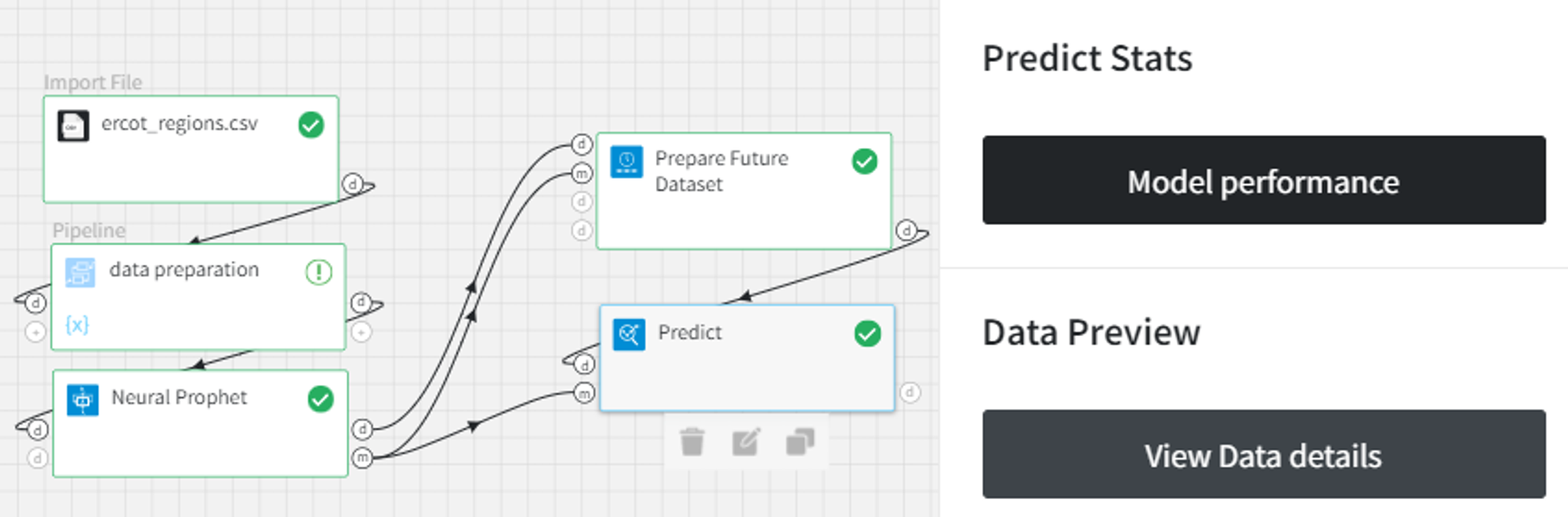
First, let’s see how to apply the brick to the simple trained model without autoregressive components.
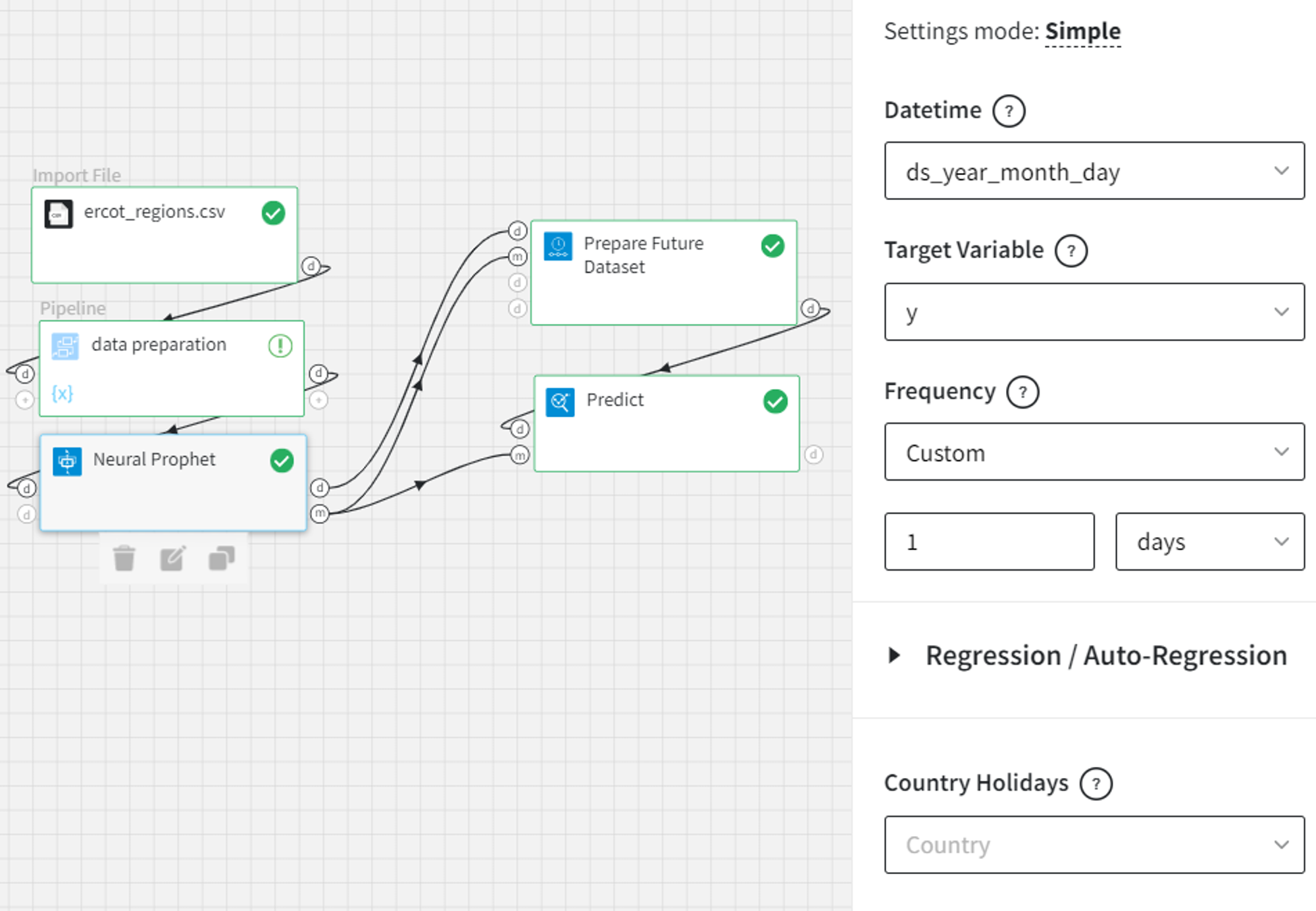
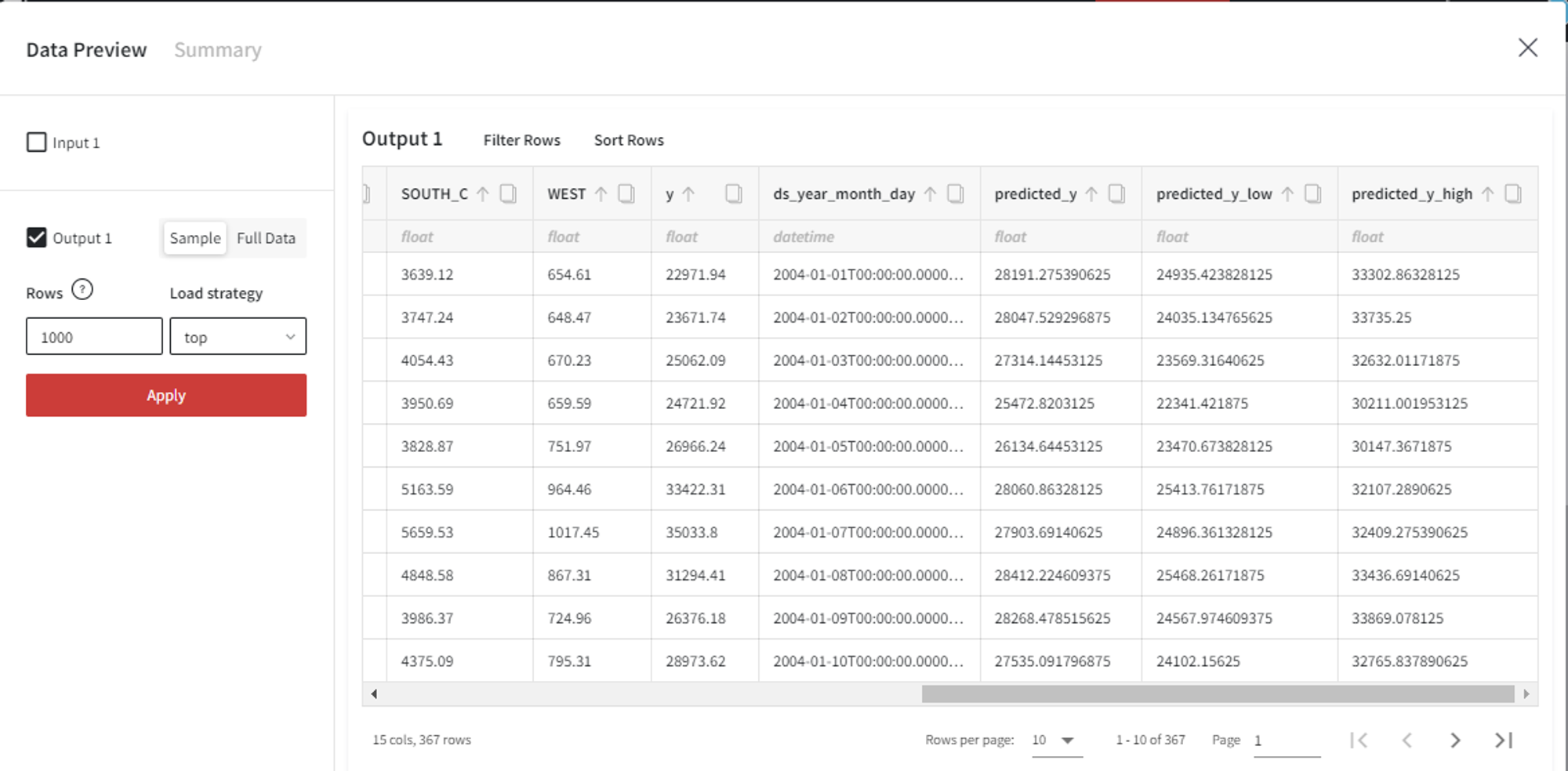
The trained model with the configuration and the output as shown above is the input to the Prepare Future Dataset brick. In the Prepare Future Dataset brick, we can select the Number of Periods parameter as 10 and include 4 Historic Predictions.
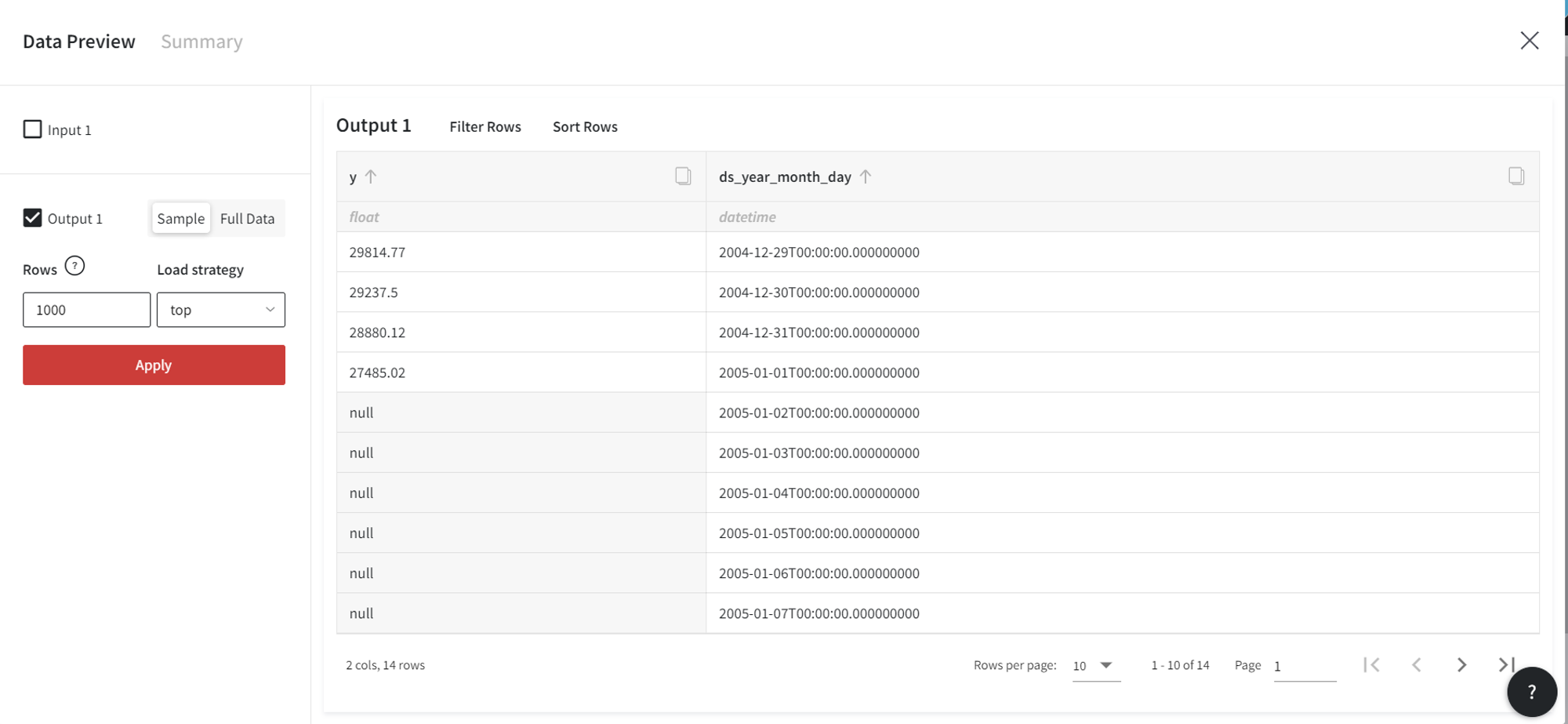
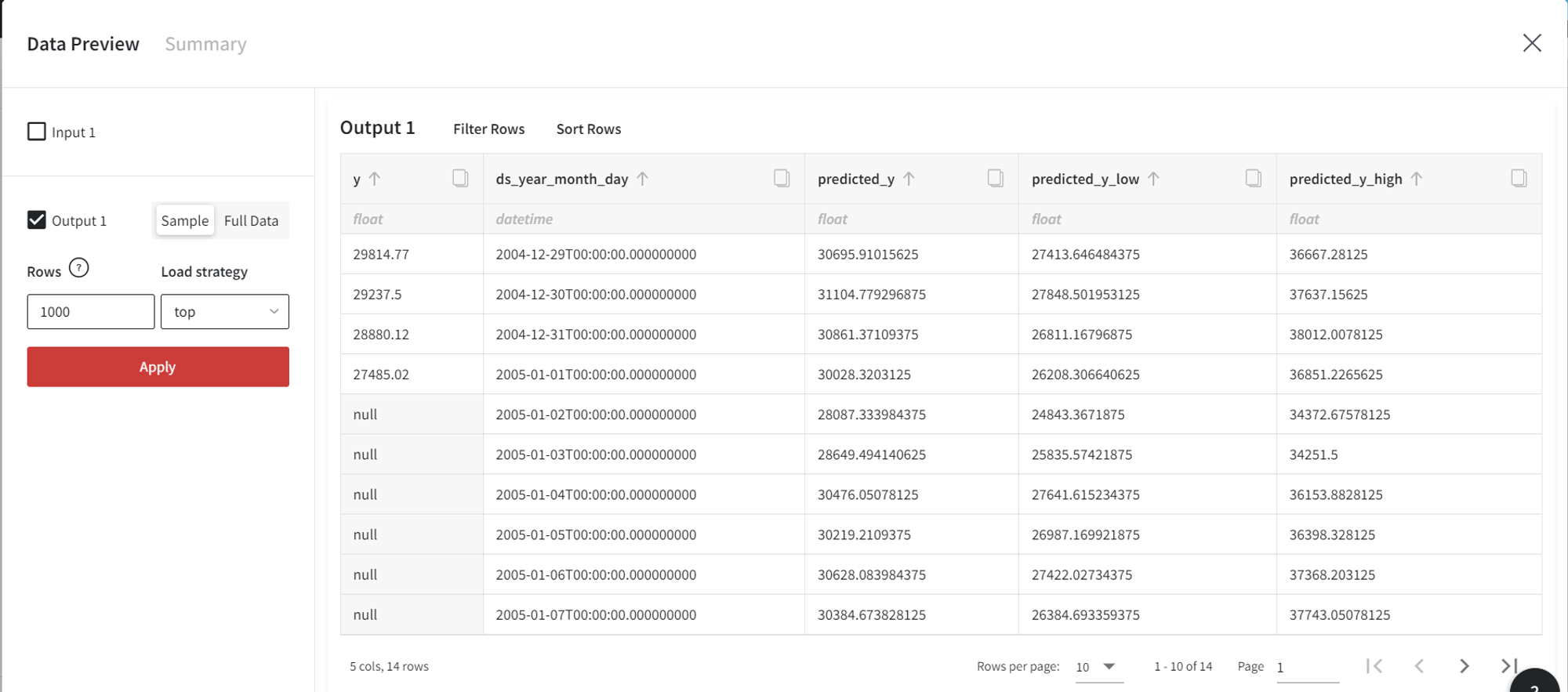
As a result, we get the following dataset with 4 rows corresponding to the historic observations and 10 future records with unknown target values.
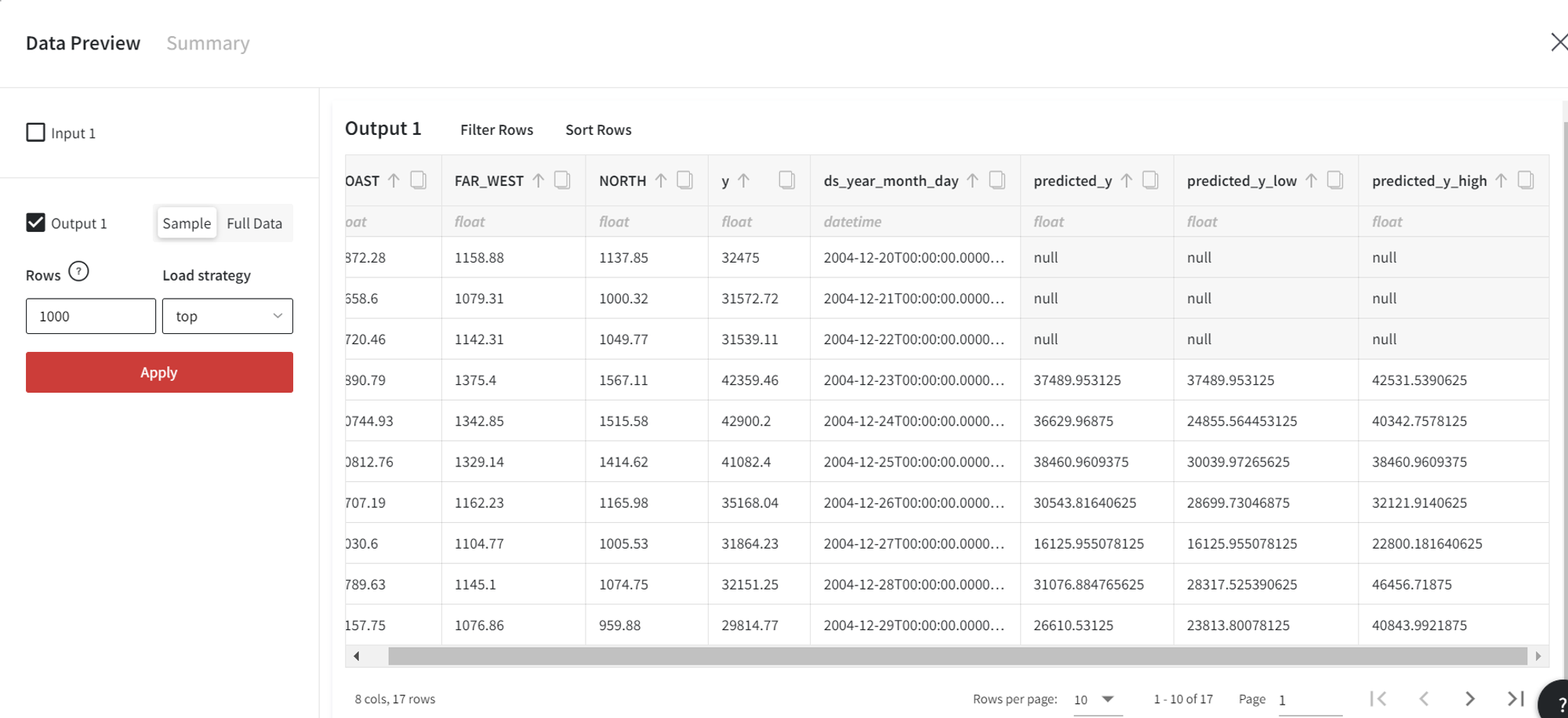
Finally, we can make model predictions for this dataset using the Predict brick.
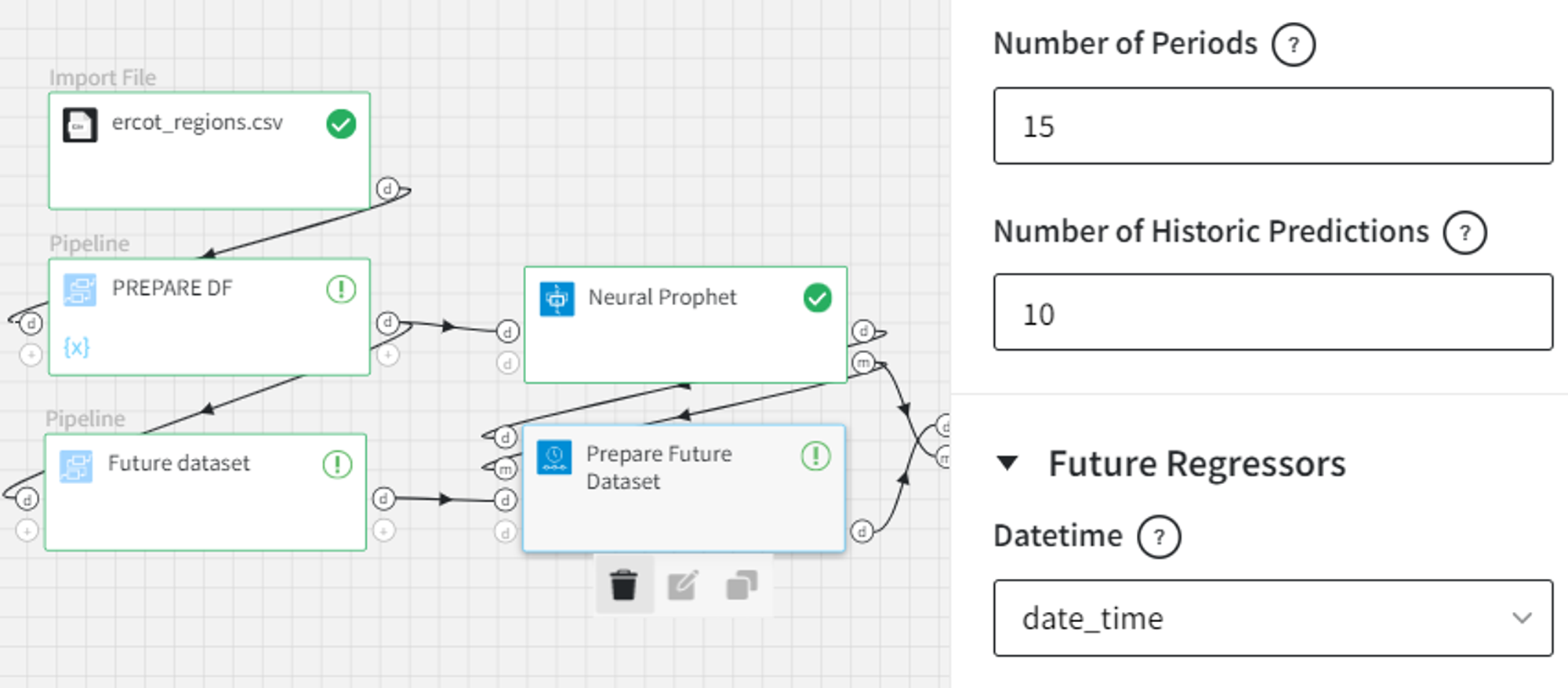
If the model contains future regressor components, we have to add the values of those components for the forecast period as the third input of the brick.
For example, the ‘COAST’ column is added to the Neural Prophet model as a future regressor and the number of forecasts is 4. Also, we add ‘NORTH’ and ‘FAR_WEST’ as lagged regressors with the number of lags equal to 3.
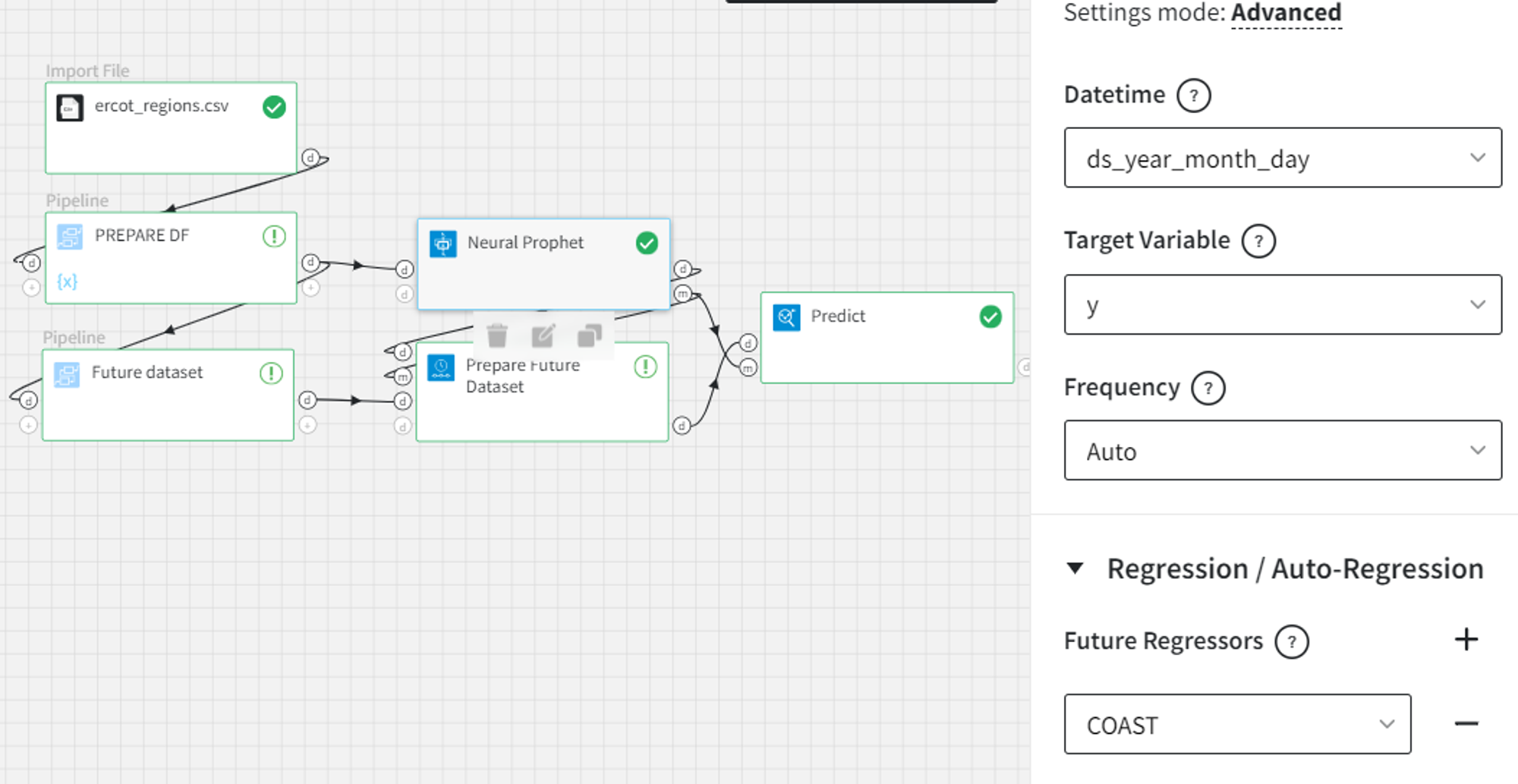
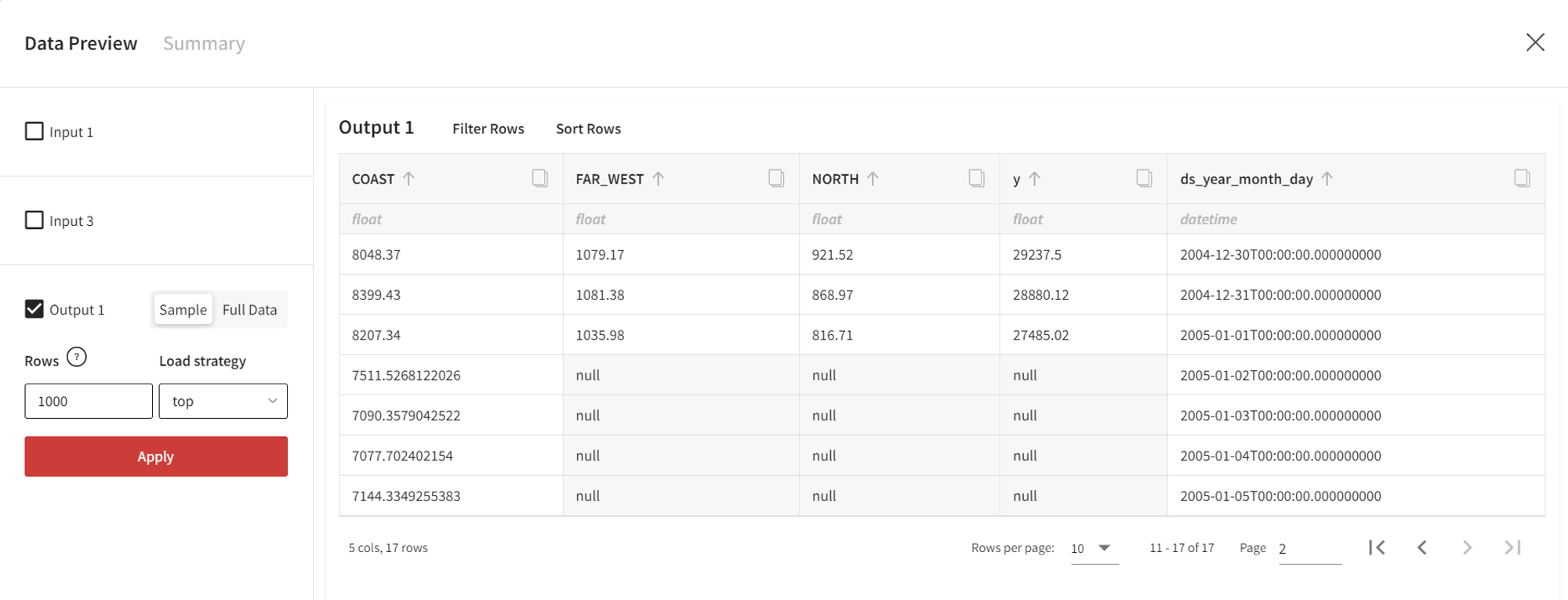
Since we have autoregressive components, the Prepare Future Dataset brick will generate 4 periods into the future. So we need to prepare a future regressors dataset with the size of at least 4 containing future regressors’ observations.
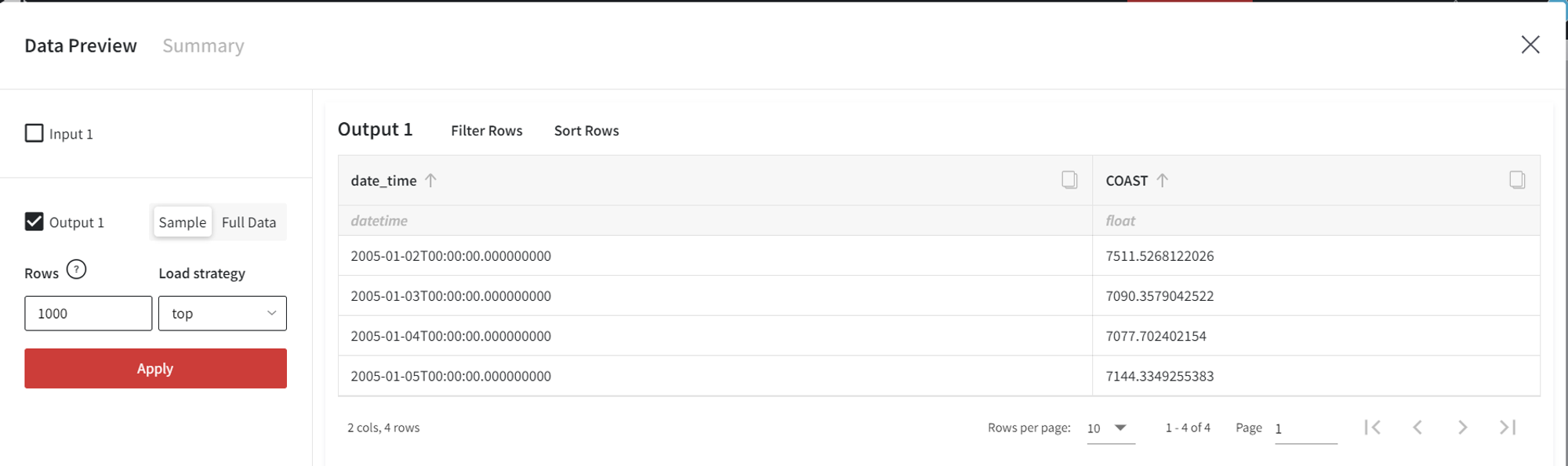
In the brick settings, we can explicitly choose a ‘Datetime’ column from the future regressors’ input dataset. If we leave it empty, we will get the dates after the last date in the input data.
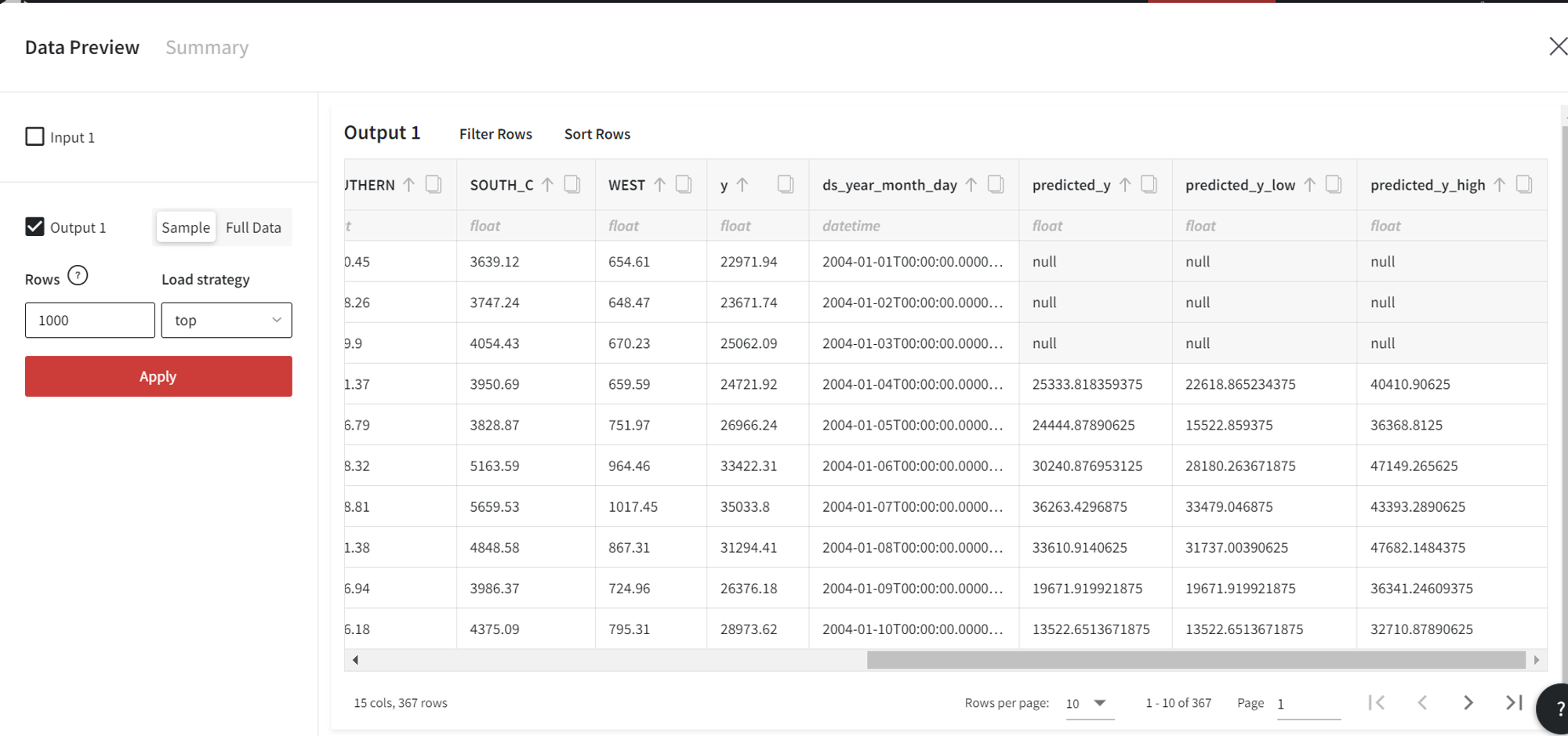
As a result, we get the dataset with a total of 17 rows (10 historic predictions, 4 forecasts, and 3 lags).
The Predict brick gives us the following predictions:
Finally, if the custom events are present in the Neural Prophet, we may add the optional events input to mark the event occurrences in the future.
In the model output, we have a binary ‘PROMO’ column indicating the events.
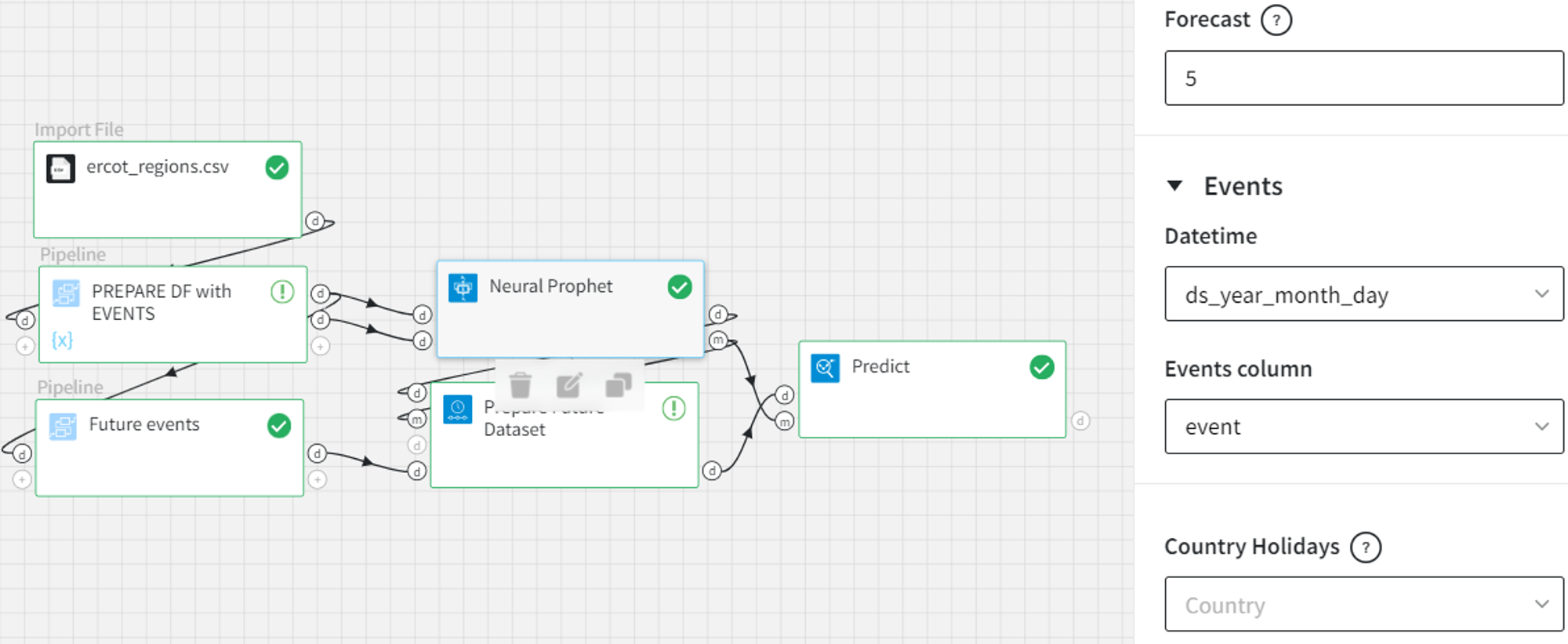
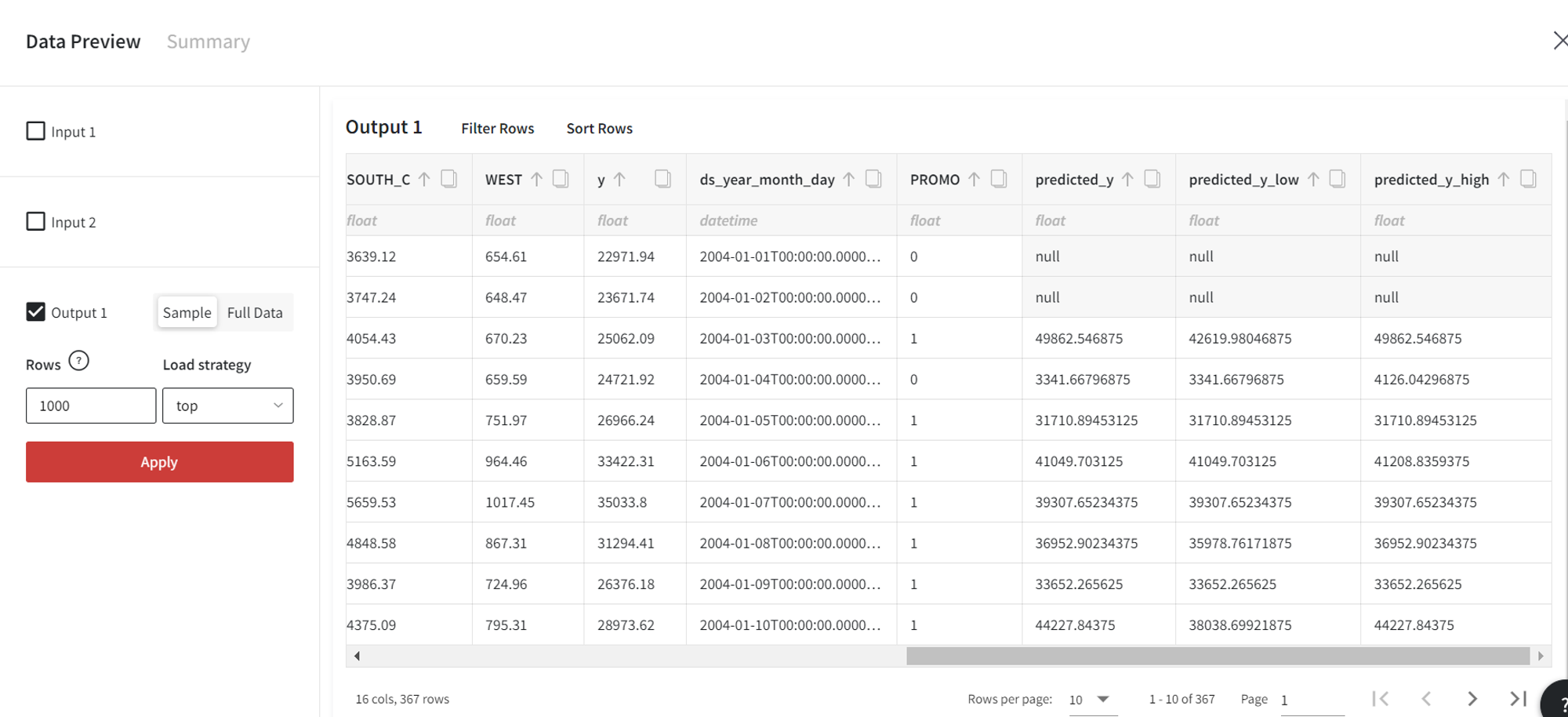
Let’s define the ‘PROMO’ events for future dates with the following dataset.
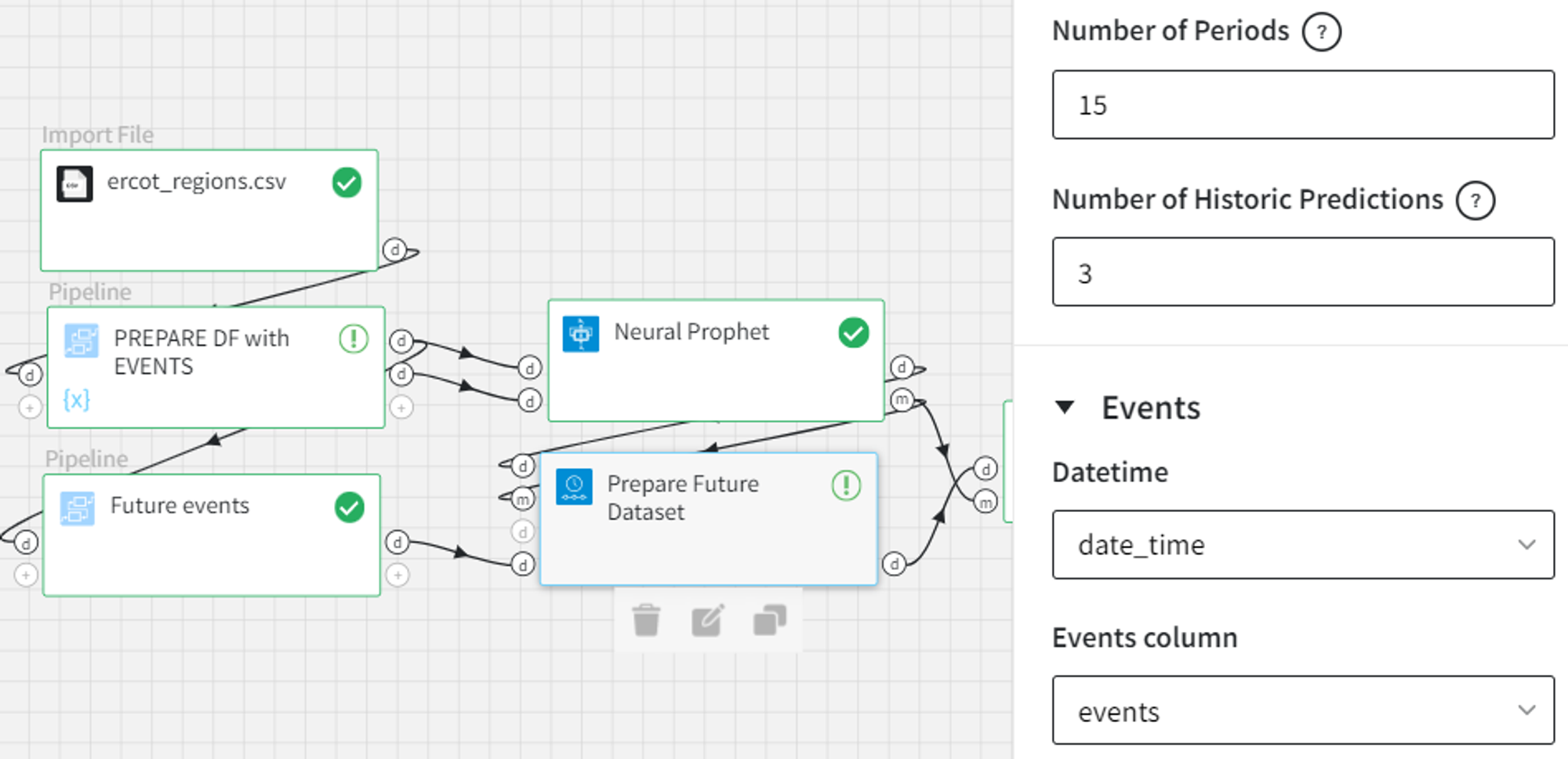
In the Prepare Future Dataset, apart from the number of periods and historic predictions, we need to choose the ‘Datetime’ and ‘Events column’ columns from the optional events input.
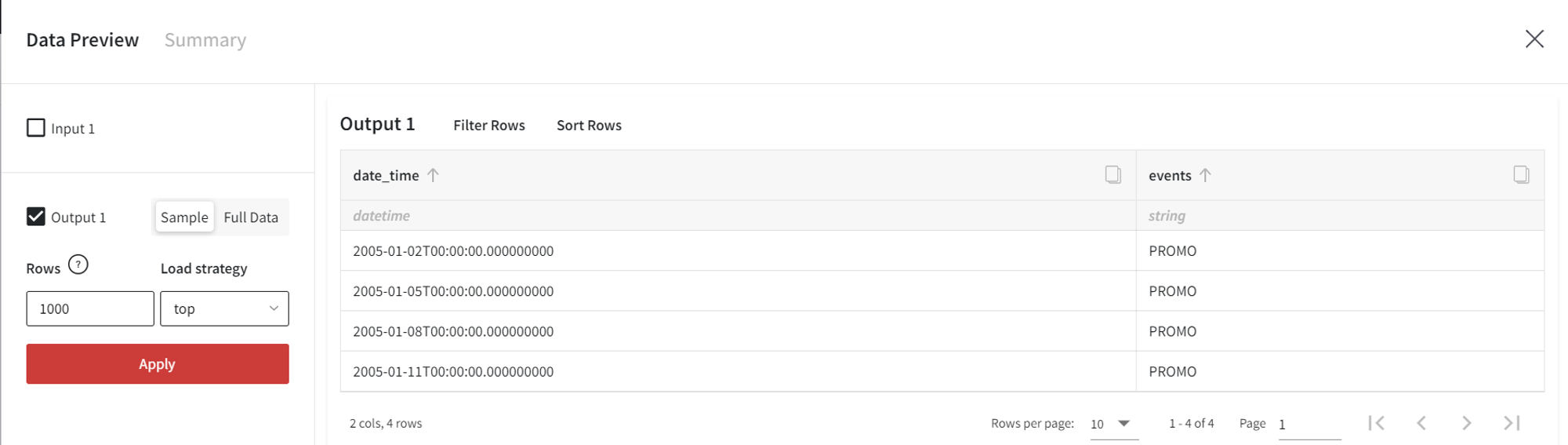
As the output, we get the next dataset:
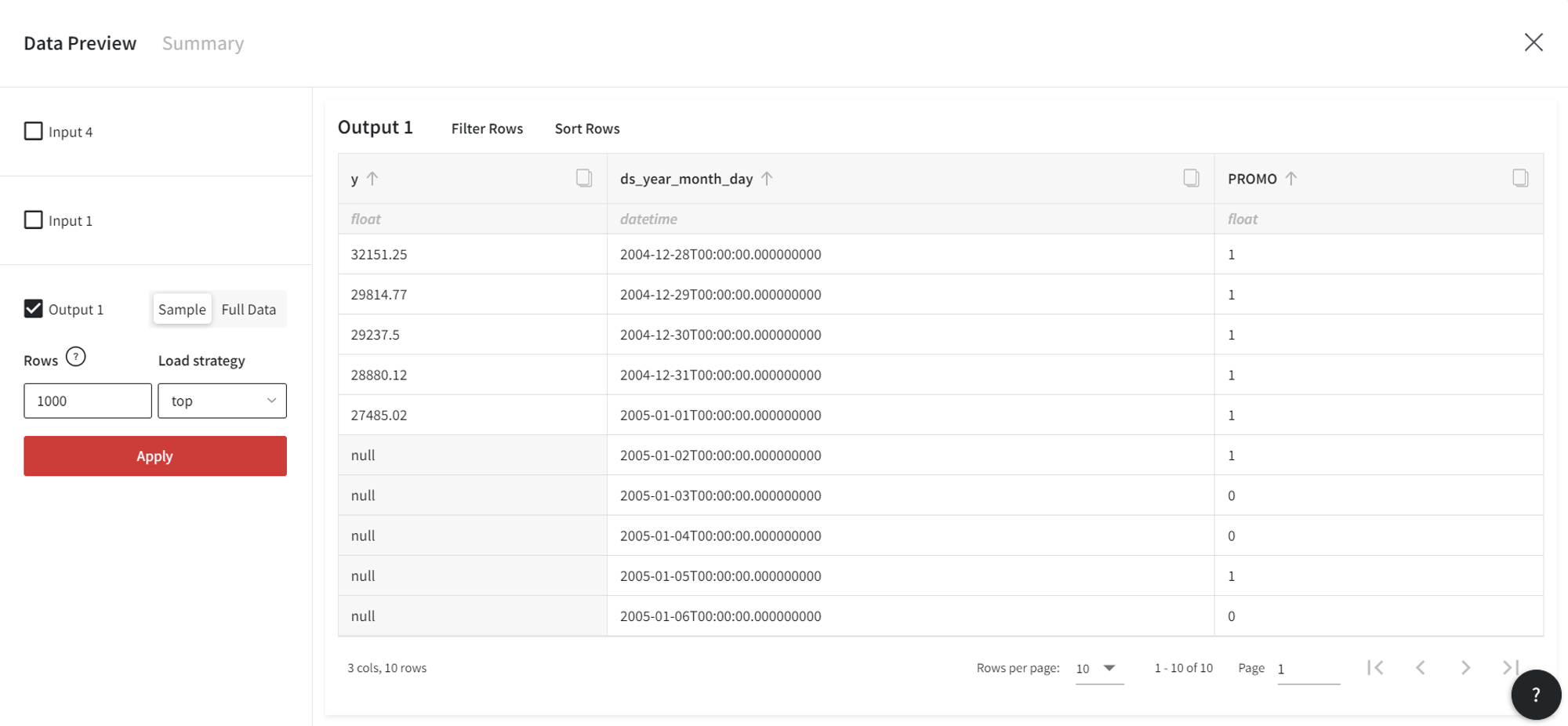
In the ‘PROMO’ column there is 1 (event happens) at the dates from the prepared events input. All the other dates are filled with 0 (no event). If we didn’t connect the events input, we would get 0 in ‘PROMO’ for all future records.